Auto-Drive Overview & Setup
Introduction
The @autonomys/auto-drive package provides a set of tools to interact with the Autonomys Auto-Drive API.
Features
- Autonomys DSN: Permanently store files on the Autonomys’ DSN (Decentralized Store Network).
- CID Management: Just like with IPFS, each upload gets its own CID (Content Identifier).
- TypeScript Support: Fully typed for an enhanced developer experience.
Authentication
All requests to the Auto-Drive APIs require authentication using an API key.
Need an API key? See our API Key Setup Guide for detailed instructions on creating your API key.
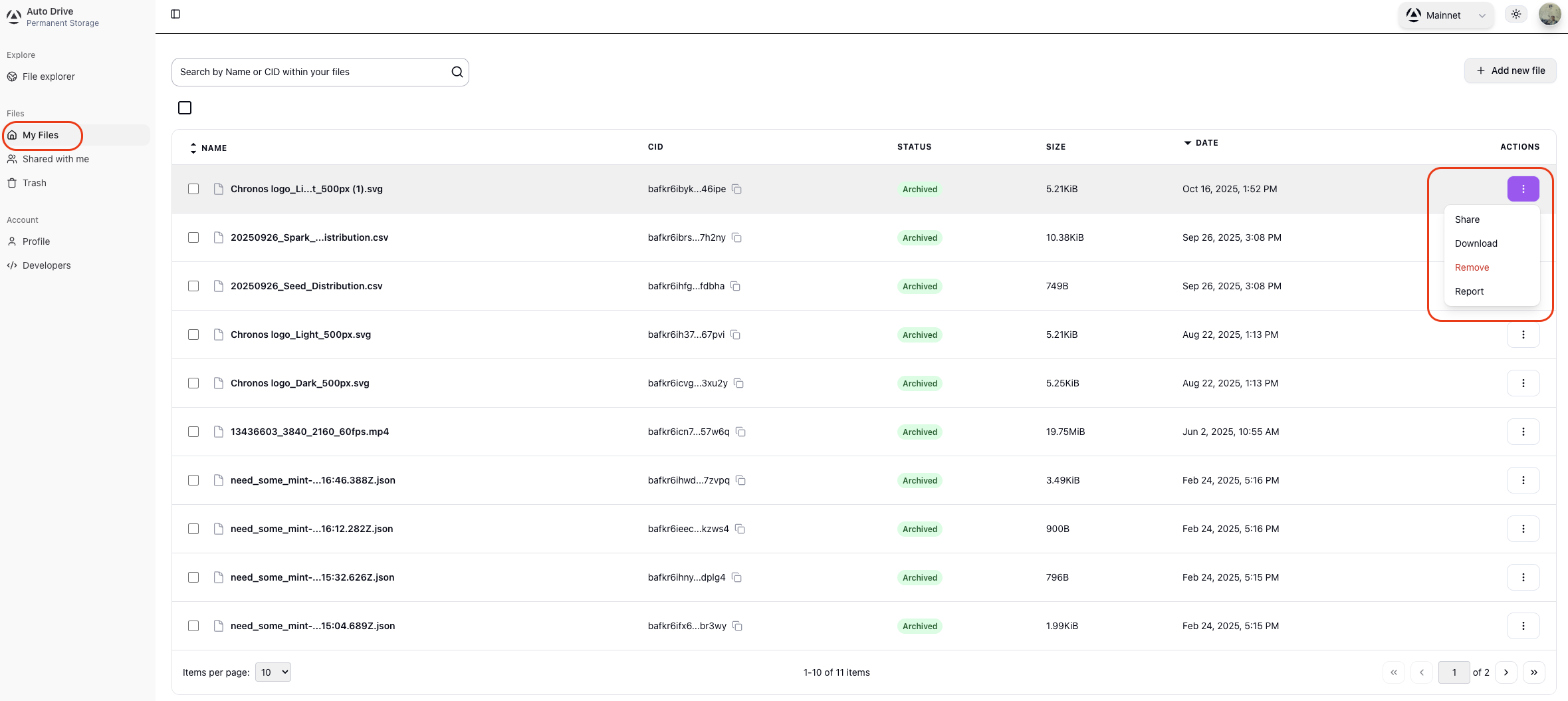
Auto Drive Dashboard
The Auto Drive dashboard provides a web interface for managing your files and account:
- View your upload and download limits
- Browse and manage your uploaded files
- Share files with others
- Create and manage API keys
Access the dashboard at Auto Drive and sign in with Google, Discord, or GitHub.

Sharing files
You can share files directly from the dashboard by clicking the Share button next to any file. You can share using a direct link or provide a user’s public ID to share all their files.
Installation
Install the package via npm or yarn:
# Using npm
npm install @autonomys/auto-drive
npm install @autonomys/auto-utils
# Using yarn
yarn add @autonomys/auto-drive
yarn add @autonomys/auto-utilsImporting
Import the auto-drive functions you need into your project:
// Import specific functions
import { fs,createAutoDriveApi } from '@autonomys/auto-drive';
import { NetworkId } from '@autonomys/auto-utils'
// Or import everything
import * as drive from '@autonomys/auto-drive';
import { NetworkId } from '@autonomys/auto-utils'Network Configuration
Auto Drive is available on Mainnet. To connect to it, you need to configure the network using auto-utils package:
import { NetworkId } from '@autonomys/auto-utils'
const api = createAutoDriveApi({
apiKey: 'your-api-key',
network: NetworkId.MAINNET
})